What is Education? Definition, Aims, and Types Explained
December 3, 2025 2025-12-03 7:26What is Education? Definition, Aims, and Types Explained

What is Education? Definition, Aims, and Types Explained
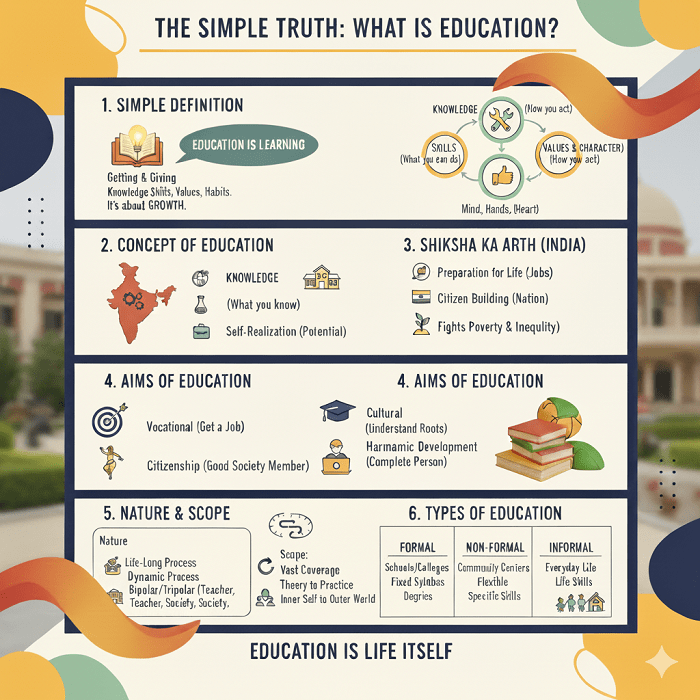
📚 The Simple Definition – What is Education?
Imagine a young child learning to tie their shoelaces. That moment—the struggle, the practice, and finally, the success—is a perfect, simple example of education.
At its very core, the meaning of education is quite simple. It is the process of getting and giving knowledge, skills, values, and habits. It is how we learn to understand the world around us and how we learn to live in it.
Think of your mind like an empty notebook. Education is the act of filling that notebook with useful information and ways of thinking.
In simple terms: Education is learning.
It’s more than just what happens in a classroom. It happens everywhere: in your home, on the playground, while watching a craftsperson work, or by reading a book under a tree.
The main idea is growth. Education is the tool that helps every person grow from being dependent on others to being a responsible, capable adult.
📘 The Heart of the Matter – The Concept of Education
To truly understand what is education, we must look beyond the definition and explore the deeper concept of education.
The concept is about change. A person who is educated is not the same as a person who is uneducated. This change happens in three main areas:
1. Knowledge (What you know)
This is the most common idea people have. It’s learning facts: who was the first Prime Minister of India, what the formula for water (H₂O) is, or how to calculate simple interest. This is the knowledge part of education. It fills your mind with information.
2. Skills (What you can do)
This is the practical side. Education teaches you skills. This could be typing on a computer, speaking another language, writing a good essay, driving a car, or solving a complicated math problem. Skills are about taking knowledge and putting it into action. They help you get a job and handle daily life.
3. Values and Character (How you act)
This is the most important, yet often forgotten, part. Education shapes your values—your beliefs about what is right and wrong. It teaches you to be honest, to respect elders, to be kind to animals, and to be a good citizen. It helps build your character. An educated person is someone who can think clearly and act rightly.
So, the full concept of education is: A purposeful process designed to develop a person’s mind (knowledge), hands (skills), and heart (values).
Shiksha ka Arth – Education in the Indian Context
In India, the word for education is Shiksha (शिक्षा). If we ask for the Meaning of Education in Hindi (Shiksha ka Arth), the answer is rich with history.
For thousands of years, the goal of Shiksha has been comprehensive. Ancient Indian education (like the Gurukul system) was not just about memorizing scriptures. It was about teaching the student how to live a balanced, ethical, and contributing life.
Today, in the modern Indian context, the core Shiksha ka Arth has three essential parts:
- Preparation for Life: Education should help people learn the skills they need to earn a living.
- Citizen Building: Education must teach people about democracy, the Constitution, and their duty to the nation.
- Self-Realization: Education must help a person understand their own potential, strengths, and weaknesses.
In India, education is seen as the greatest tool to fight poverty and inequality. It is the ladder by which a person from any background can climb and improve their life.
🎯 Setting the Target – The Aims of Education
If education is a journey, then the aims of education are the destinations. We don’t just learn things for no reason; we learn them because we have goals.
What are the main goals—the aims—that education systems around the world, especially in India, try to achieve?
1. The Vocational Aim (Getting a Job)
This is the most practical aim. The goal is to make a student capable of earning a living. Education teaches them specific, useful skills—how to be a mechanic, a doctor, a teacher, or a software engineer. This aim helps the student become economically independent.
2. The Cultural Aim (Understanding Your Roots)
Education teaches us about our culture, history, art, music, and traditions. In a country as diverse as India, this aim is important. It helps students appreciate different languages and customs, which helps in national unity.
3. The Citizenship Aim (Being a Good Member of Society)
This aim teaches students to respect laws, vote responsibly, help the community, and stand up for justice. It turns a student into a good citizen who contributes positively to the country.
4. The Harmonic Development Aim (The Complete Person)
This is the highest goal. It means developing all parts of a person—their body (physical education), their mind (intellectual education), and their spirit (moral education). The aim is to create a complete, balanced, and happy human being.
In short, education aims to make a person Independent, Informed, and Integrated (a good member of society).
🌳 What Education is made of – The Nature and Scope of Education
When we talk about the nature and scope of education, we are asking: What is the character of this process, and how wide does it reach?
The Nature of Education:
The essential nature of education can be seen in three key ways:
- A Life-Long Process: Education does not stop when you graduate from school or college. It starts from the day you are born and continues until you die. Learning new things, adapting to technology, and gaining experience are all part of this continuous process.
- A Bipolar or Tripolar Process:
- Bipolar View: Many thinkers see education as a process with two main poles: the Teacher and the Student. The teacher’s job is to influence and guide the student.
- Tripolar View: A more modern and complete view adds a third pole: the Society or Environment. A student is taught by the teacher, but also by their friends, their family, the news they read, and the culture they live in.
- A Dynamic Process: Education is always changing. What was taught 100 years ago is different from today. As society, technology, and knowledge change, so does the way we educate.
The Scope of Education:
Scope of education means how big or how wide its coverage is. The scope is huge —it touches every part of human life.
- From Cradle to Grave: It covers all stages: pre-primary, primary, secondary, higher education, adult education, and lifelong learning.
- From Theory to Practice: It includes all subjects: science, math, literature, history (theory), and vocational skills like carpentry or computing (practice).
- From Inner Self to Outer World: It covers inner development (moral and spiritual education) and outer development (social and national education).
Essentially, the scope of education is the scope of human life itself. Everything we learn, from how to cook a meal to how to send a rocket to space, falls under the scope of education.
🏫 The Different Pathways – Types of Education
When we ask “what is education?”, we find that it comes in three main forms, or types of education, each playing a vital role in our development.
1. Formal Education
This is the type of education everyone recognizes.
- Where it happens: In schools, colleges, and universities.
- Key Features: It has a fixed timetable, a written curriculum (syllabus), specific rules, professional teachers, and results in certificates or degrees (like a B.A. or M.Sc.).
- Goal: To give systematic, organized, and graded knowledge to help you progress in a career.
- Example: Attending a history class in a government high school.
2. Non-Formal Education
This type is organized, but it is flexible and often happens outside the regular school system.
- Where it happens: Community centers, NGOs, correspondence courses, or distance learning centers.
- Key Features: It is designed to meet the needs of a specific group, like adults who didn’t finish school or people who need a specific skill quickly. It has flexible timing and no strict age limit.
- Goal: To provide literacy, specific vocational skills, or continuing education to a focused group.
- Example: An evening class for literacy, or an online coding course.
3. Informal Education
This is the most natural and continuous type of education.
- Where it happens: Everywhere—at home, on the street, at the workplace, in the market.
- Key Features: It is unplanned, spontaneous, and has no curriculum, teacher, or certificate. It is the education you get through life experience.
- Goal: To help a person adjust to their environment and learn daily life skills and social manners.
- Example: A child learning to be polite by watching their parents, or a person learning how to budget money by managing their monthly salary.
All three types of education are important. Formal education gives you a degree, Non-Formal gives you specific skills, and Informal education teaches you how to live.
✅ Conclusion:
The simple answer to the question “What is Education?” remains the most powerful: It is the continuous, lifelong process of becoming a better version of yourself.
It is the light that removes the darkness of ignorance. In India, Shiksha is the promise of a better tomorrow, not just for the individual, but for the entire nation. By understanding the simple definitions, the core concept, the high aims, and the different types of education, we can all work to make this powerful process reach every child and adult, giving them the knowledge, the skills, and the character to succeed. Education is not merely a preparation for life; education is life itself.
❓ FAQs
1. What is the simplest way to define education?
The simplest way to define education is that it is the process of lifelong learning. It’s how people get and give skills, knowledge, habits, and values. Think of it as a tool that helps you understand the world and develop yourself completely—not just your mind, but also your character and your ability to do things. It starts when you are very young and keeps going until you are very old, because we never stop learning new things from our experiences.
2. Is education only about getting high marks in school?
No, education is much bigger than just getting high marks. While good marks show you have learned the facts and passed the tests, true education is also about building skills and strong values. It means you can solve real-life problems, treat people with respect, and think for yourself. A person with high marks but poor manners is not fully educated. True education aims to make you a complete, responsible, and capable human being, not just a successful test-taker.
3. What is the difference between “knowledge” and “skills” in education?
Knowledge is the information you have in your mind, and skills are what you can practically do with that information. For example, knowing the rules of cricket is knowledge. Being able to hit the ball and score a run is a skill. Education gives you both. You need the knowledge (like math formulas) to understand the world, but you need the skills (like coding or writing) to get a job and be successful in your daily life. Both are essential parts of the learning process.
4. What does the Hindi word “Shiksha” (शिक्षा) truly mean in the Indian context?
Shiksha (शिक्षा) is the Indian word for education, and its meaning goes beyond simple schooling. Traditionally and currently, it means education that helps a person’s complete development. In India, Shiksha ka Arth is seen as a way to fight poverty, build the nation, and help every person realize their full potential. It’s expected to make you independent, so you can earn a living, and also make you a good citizen who respects others and follows the country’s laws.
5. Why are values and character important parts of education?
Values and character are perhaps the most important parts because they guide how you use your knowledge and skills. Education teaches you what is right and wrong. It helps you develop good character traits like honesty, kindness, and hard work. If a very smart person (high knowledge) has bad values (like being selfish or dishonest), their education can actually hurt society. Therefore, true education must train the heart to be good, along with training the mind to be smart.
6. What is the main “aim” or goal of education?
The main aim of education is to prepare a person for all aspects of a successful and meaningful life. This includes the vocational aim, which helps you get a job and become financially independent. It also includes the citizenship aim, which teaches you to be a responsible member of society. Most importantly, it aims for harmonic development, meaning it develops your body, mind, and spirit so you become a balanced, happy, and contributing person to your family and nation.
7. Does education stop after I finish college?
Absolutely not! Education is a continuous, life-long process. When you finish college, you finish the formal education stage, but you enter the world of informal education. You constantly learn new things at your job, from new technologies, from raising a family, or just by reading and watching the news. Since the world is always changing, you must keep learning and adapting your skills throughout your entire life to stay relevant and successful.
8. What is the difference between Formal, Non-Formal, and Informal education?
These are the three main types of education based on how they are organized. Formal education is structured, happens in schools/colleges, has a fixed syllabus, and gives you a degree. Non-formal education is organized but flexible, like evening classes or online courses for specific skills, and is often for adults. Informal education is the learning you get naturally and unplanned, every day, from life experiences, like learning manners from your parents or fixing a simple appliance.
9. Why is education considered a “dynamic process”?
Education is called a dynamic process because it is always moving, changing, and adapting to the world. It is not fixed. 100 years ago, students did not learn about computers or the internet, but today, these are essential. As science and society change, what we teach and how we teach it must also change. The education system has to update its methods and subjects constantly to make sure students are ready for the modern world and the future.
10. Does education only happen inside a classroom?
No, education has a very wide scope and happens everywhere, not just inside a classroom. While the classroom is where you get formal education (structured lessons and facts), you get the most important informal education outside. You learn social skills from your friends, responsibility from your parents, and life lessons from every experience you have. The scope of education includes everything that shapes your knowledge, character, and ability to deal with the world around you.






